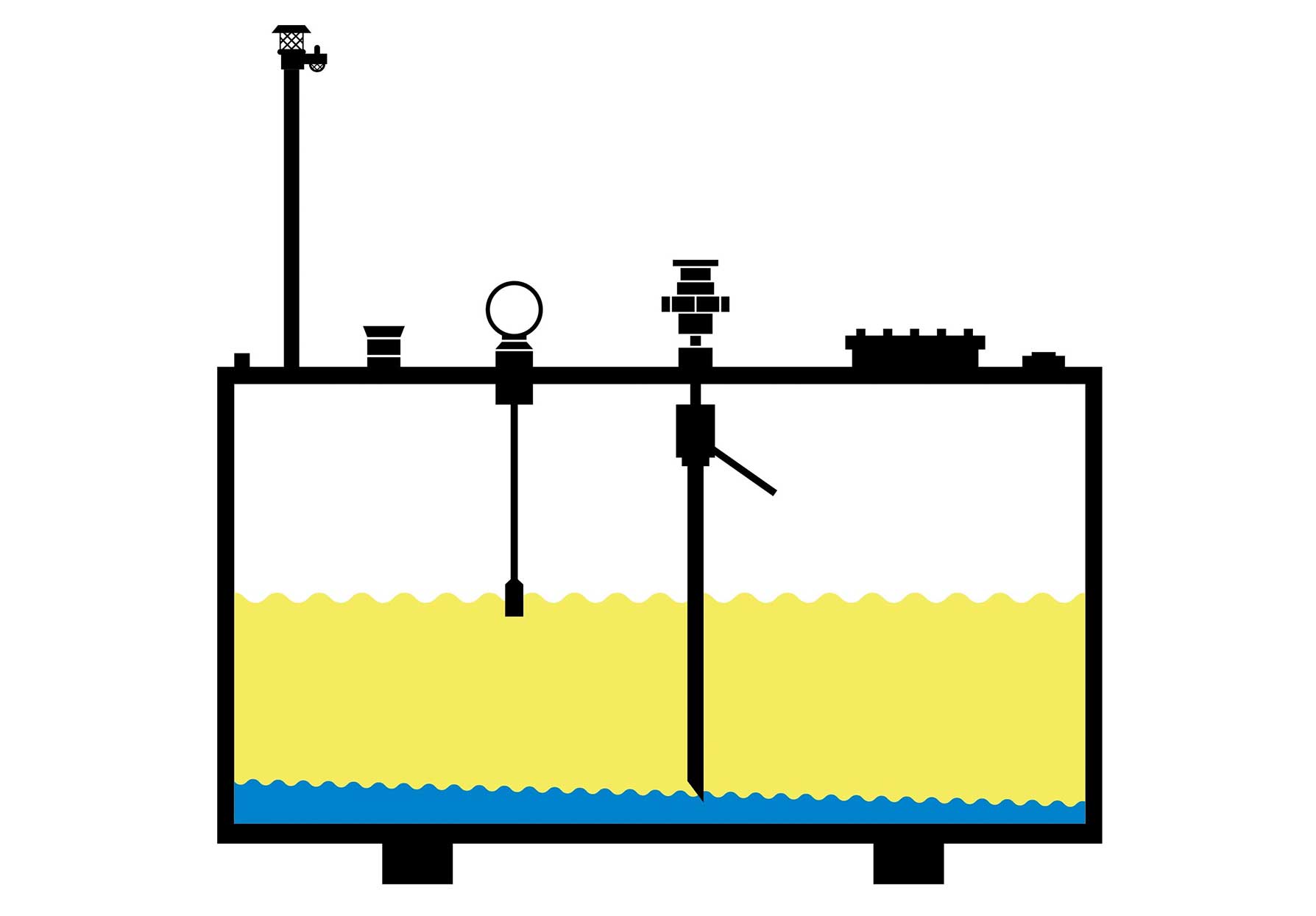
Poor operations and maintenance procedures for monitoring and removing water from storage tank systems can lead to a number of risks, from fuel quality degradation and resulting poor vehicle performance, to microbial contamination and damage to the entire storage system.
All storage tank systems, both underground and aboveground, constructed of any material, and storing nearly any product—gasoline, diesel, residential and commercial heating oils, aviation jet fuel, and others—may be affected.
The potential for damage applies not only to the tank, but also to the entire storage system. And these risks can affect your profits.
Today’s fuels are more susceptible to moisture separation and accumulation. Also, removing lead from gasoline and sulfur from diesel has had the side effect of allowing microbial growth to occur more readily, since lead and sulfur inhibit microbial activity.
Ethanol and biodiesel are important in today’s fueling network. But allowing water to remain in these storage systems can cause fuel separation, fuel degradation, and non-metallic equipment compatibility concerns.
For all these reasons, it’s more important than ever to conduct regular inspection and maintenance of your entire UST fuel storage system.
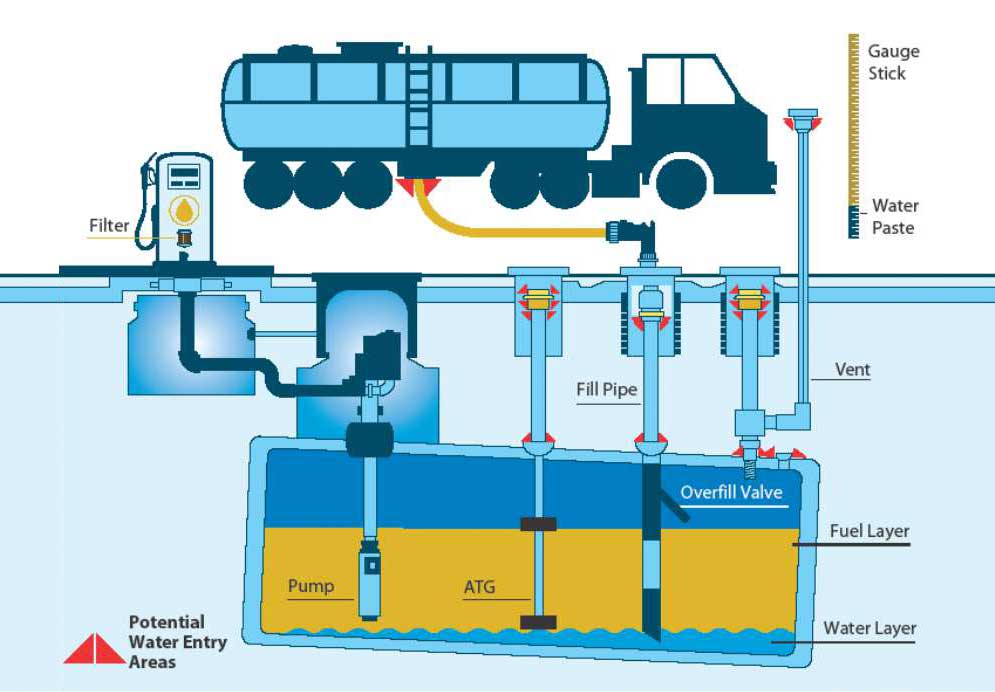
Water entry points in your fuel storage tank system
Protect Your Fuel Product
- Engine manufacturers have zero tolerance for water in fuel.
- Inspect your storage tank system frequently.
- Check for water with automatic and manual tank gauging.
- Remove and properly dispose of any water found in accordance with industry recommended practices.
- Investigate the source of any water found.
- Audit the fuel or product delivery process and the water content.
- Use water-sensitive filters and watch for slowed-down fueling or dispensing.
- Hire a professional to treat storage tanks with biocide on a regular basis if microbial activity is evident or suspected.
- Employ a qualified professional to periodically examine the inside of the tank.
- Remove water and sludge and periodically clean the tank, in accordance with industry recommended practices.
Take the protective measures described to monitor and inspect your fuel storage system. Learn how to inspect your system:
- Underground Storage Tanks (USTs), US EPA Office of Underground Storage Tanks
- Keeping Water Out of Your Storage System
- Tank Integrity Management Course
- Diesel Fuel Storage and Handling Guide
Resources
- Recommended Practice for Storage Tank Maintenance (R111)
- Standard for Inspection, Repair, and Modification of Shop-fabricated Underground Tanks (SP131)
- PEI RP900: Recommended Practices for the Inspection and Maintenance of UST Systems
- API RP 1621: Bulk Liquid Stock Control at Retail Outlets, Appendix D Water Gauging Procedure
- ASTM D6469 Standard Guide for Microbial Contamination in Fuels and Fuel Systems
- ASTM D975 Standard Specification for Diesel Fuel